
Ansai Integrated Experimental Station on Water and Soil Conservation - China
Ansai Integrated Experimental Station on Water and Soil Conservation is a part of Chinese Ecosystem Research Network, which located in the typical loess hilly and gully region and situates near the center of the Loess Plateau in the Shaanxi Province. The loess-derived soils are fertile but extremely susceptible to erosion. Soil erosion in the study area is much higher than that in the southern part of the Loess Plateau. The climate belongs to transition zone of warm temperate semi-humid to semi-arid, which is dry and windy in spring, hot and rainy in summer, and dry and cold in winter. The mean annual temperature is 8.8 °C. The minimum and maximum temperatures are −23.6 °C in February and 36.8 °C in July. The frost-free period is 157 days. The mean annual precipitation is 505 mm, 70% of which falls between July and September in the form of short heavy storm. The soil is silt loam with the contents of sand, silt, and clay being 24%, 65%, and 11%. Ansai station mainly focus on vegetation rehabilitation, monitoring and assessment of rehabilitation, and monitoring in watershed.

Accumulation - Andrea Molina Cuadro - Air Mines and Burial Sites

Ecological Park of Soil and Water Conservation in Jiangxi Province.

The Heihe Integrated Observatory Network: A Basin‐Scale Land Surface Processes Observatory in China - Liu - 2018 - Vadose Zone Journal - Wiley Online Library
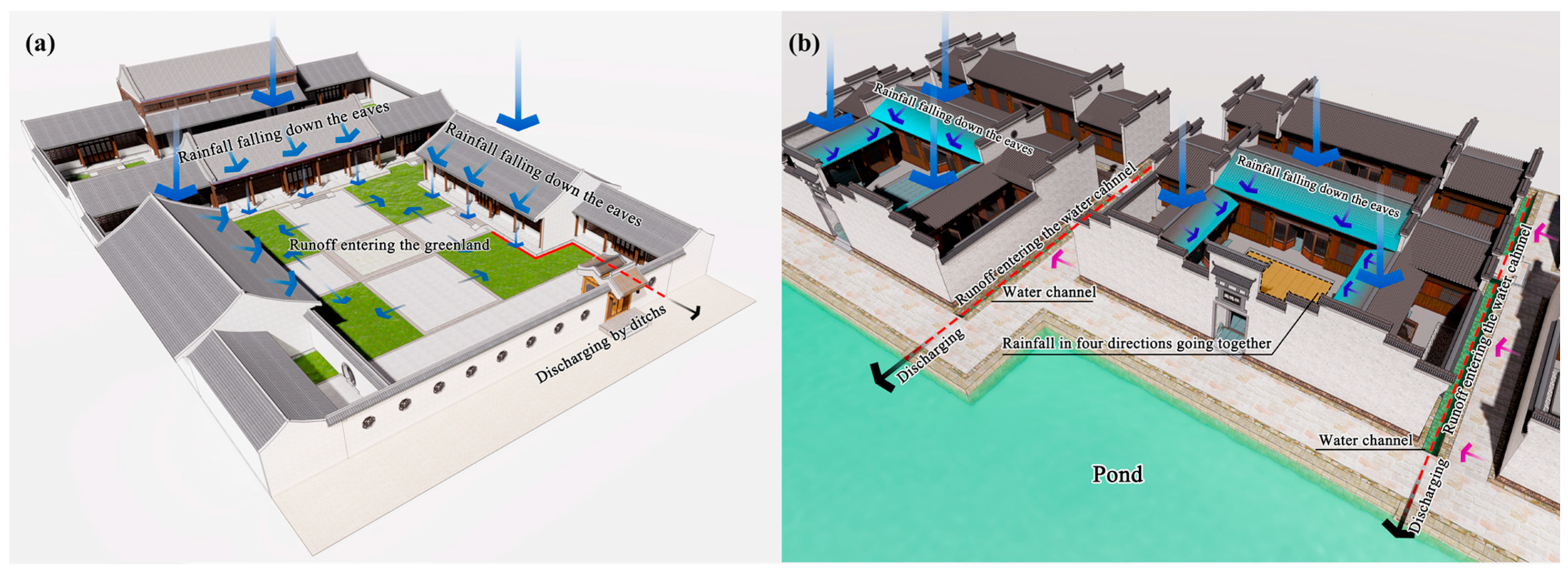
Water, Free Full-Text

Full article: Integrative technology hubs for urban food-energy-water nexuses and cost-benefit-risk tradeoffs (II): Design strategies for urban sustainability

Prof. John Langford Visits Ansai Station----Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Chinese Academy of Sciences & Ministry of Water Resources
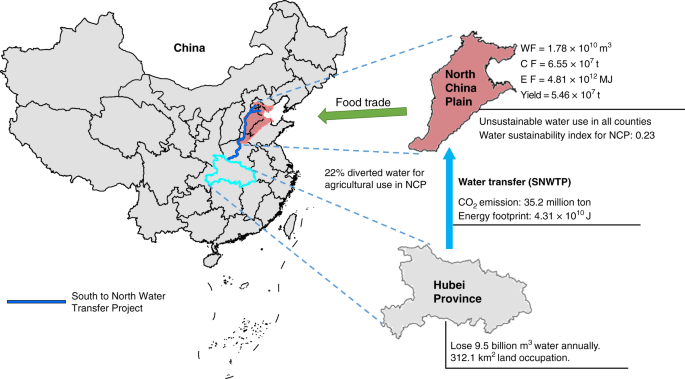
Impacts of irrigated agriculture on food–energy–water–CO2 nexus across metacoupled systems

The 2023 China report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: taking stock for a thriving future - The Lancet Public Health
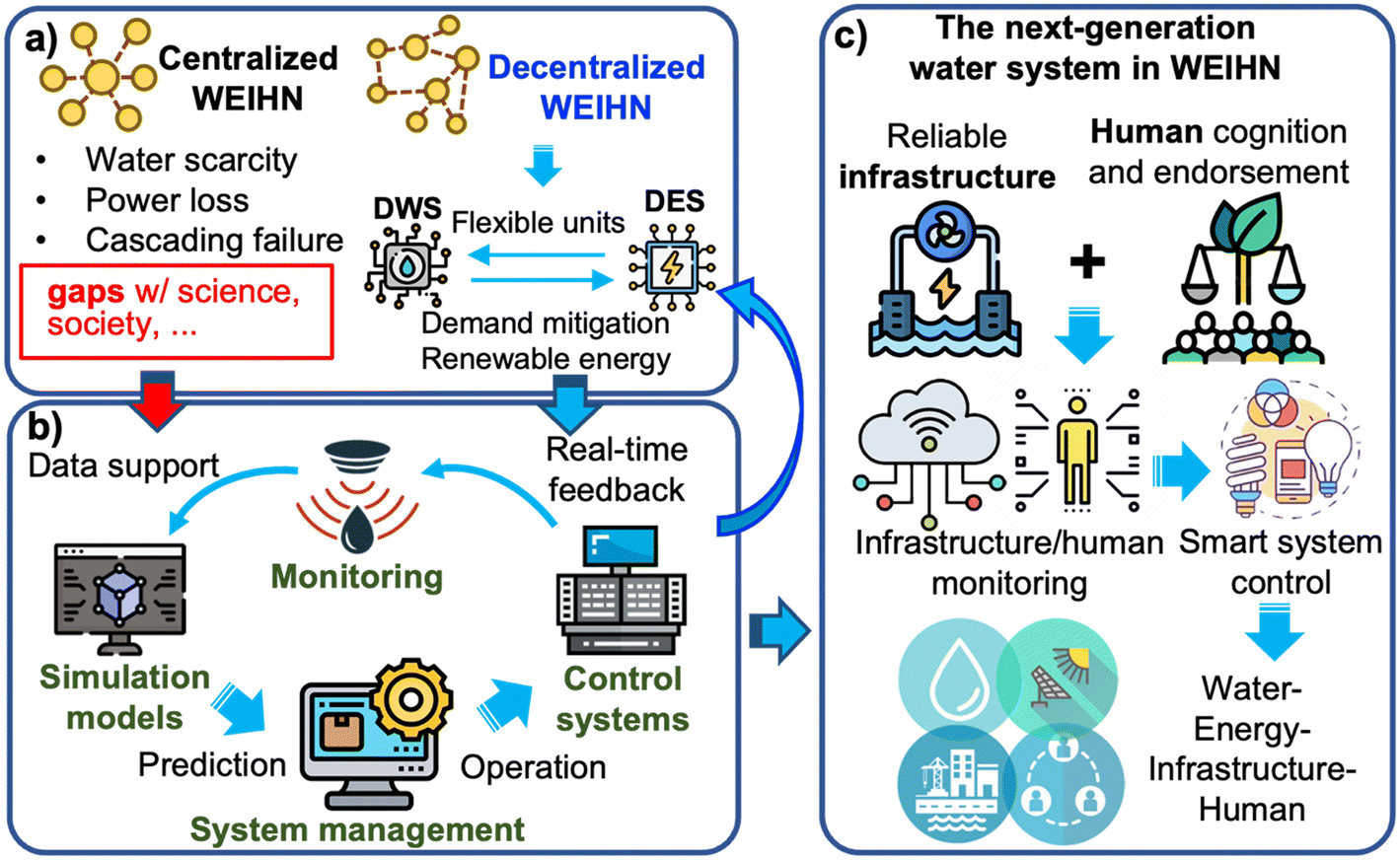
Next generation decentralized water systems: a water-energy-infrastructure-human nexus (WEIHN) approach - Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D3EW00506B
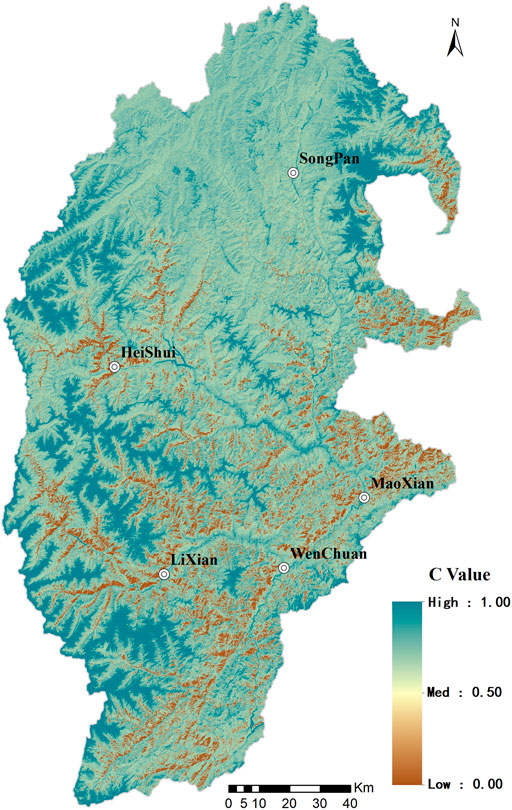
Frontiers Remote Sensing Quantitative Research on Soil Erosion in the Upper Reaches of the Minjiang River

Cropping System Diversity Effects on Nutrient Discharge, Soil Erosion, and Agronomic Performance








